₹600.00
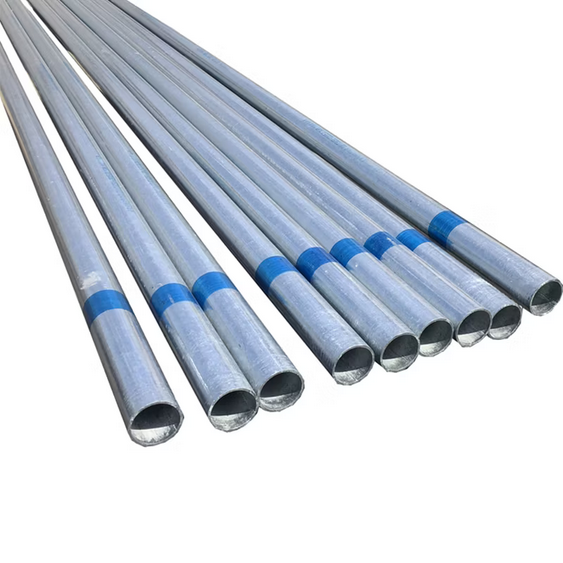
High-quality GI Pipes with superior zinc coating for rust-free performance. Ideal for plumbing, water supply, and structural applications. Available in top brands like Jindal Star, Apollo, and more — delivered across India.
Additional information
| Length | 6 Metre |
|---|---|
| Brand | Jindal Star, Jindal Hissar, Ravindra, Apollo |
Enquiry Form
Fill out the form below and we'll get back to you as soon as possible.
Looking for strong, corrosion-resistant piping solutions? Our GI Pipes (Galvanized Iron Pipes) are the trusted choice for plumbing, water supply, structural, and industrial applications across India. These pipes are made by coating mild steel with a layer of zinc, which protects against rust, weather, and wear — making them ideal for both indoor and outdoor use.
We Deliver PAN India, supplying high-quality GI Pipes to contractors, builders, engineers, and industries from metro cities to rural projects.
✅ Key Features of Our GI Pipes:
Corrosion-Resistant: Zinc coating provides long-term protection from rust and moisture.
Durable & Strong: Suitable for heavy-duty applications and high-pressure flow.
Smooth Flow: Uniform inner surface ensures minimal friction and smooth water/gas flow.
Long Lifespan: Designed to perform for years with minimal maintenance.
Versatile Applications: Plumbing, irrigation, scaffolding, fencing, and structural use.
🔧 Applications:
Water supply lines (residential, commercial, municipal)
Gas piping and compressed air systems
Firefighting systems
Structural and scaffolding support
Agricultural irrigation and borewell casing
🏷️ Brands We Deal In:
We stock and supply GI Pipes from India’s most trusted manufacturers:
Jindal Star
Jindal Hissar
Ravindra Pipes
Apollo Pipes
These brands are known for their ISI-marked, high-quality GI pipes that meet Indian and international standards.
🔵 Round GI Pipes
Our inventory includes a wide range of Round GI Pipes, known for their high strength and durability. Ideal for fluid transport and structural use, these pipes are available in various diameters and wall thicknesses, ensuring the right fit for every project.
🚚 Nationwide Delivery
No matter where your project site is — from big cities to remote areas — we’ve got you covered. Our logistics network ensures fast, reliable delivery across India, minimizing downtime and keeping your project on track.
Related Products
Related products
Customer Reviews
“A review from a customer who benefited from your product. Reviews can be a highly effective way of establishing credibility and increasing your company's reputation.”

Customer Name
“A review from a customer who benefited from your product. Reviews can be a highly effective way of establishing credibility and increasing your company's reputation.”

Customer Name
“A review from a customer who benefited from your product. Reviews can be a highly effective way of establishing credibility and increasing your company's reputation.”

Customer Name